Introduction
Smart investors know that real estate tax strategies play a crucial role in maximizing profits and minimizing tax burdens. Whether you’re a seasoned real estate investor or just starting, understanding how to legally reduce your tax liability can help you keep more of your earnings. With the right real estate tax strategies, you can take advantage of deductions, depreciation, tax-deferred exchanges, and other powerful methods to build wealth efficiently.
Taxes can significantly impact real estate returns, but proper planning can make all the difference. Investors who implement real estate tax strategies can benefit from various IRS-approved deductions, lower capital gains tax rates, and legal loopholes that make real estate one of the most tax-advantaged investments. Knowing how to navigate the tax code can transform a good investment into a great one.
In this guide, we’ll explore the most effective real estate tax strategies that savvy investors use to save big. From depreciation and 1031 exchanges to Opportunity Zones and rental property deductions, you’ll learn how to structure your investments to pay less in taxes while maximizing your financial growth.

Understanding Real Estate Tax Strategies
Real estate tax strategies are essential for investors who want to maximize their profits and minimize tax liabilities. With the right real estate tax strategies, investors can take advantage of deductions, credits, and tax deferral opportunities that significantly impact their bottom line. Whether you are a seasoned investor or just getting started, understanding real estate tax strategies can help you build long-term wealth.
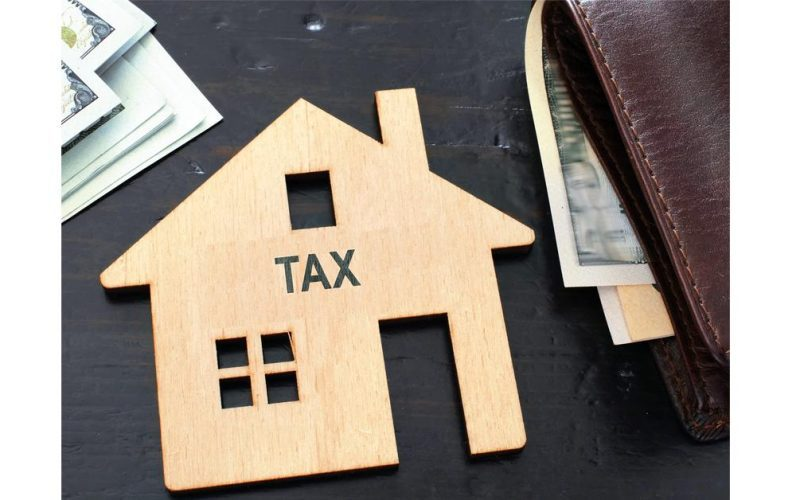
One of the key benefits of leveraging real estate tax strategies is the ability to offset rental income with depreciation deductions. Depreciation allows investors to account for property wear and tear over time, reducing taxable income. By incorporating real estate tax strategies that maximize depreciation deductions, investors can lower their tax burden while still generating steady cash flow.
Another vital component of real estate tax strategies is structuring investments to qualify for lower capital gains taxes. Long-term capital gains tax rates are significantly lower than ordinary income tax rates, making it crucial to hold properties for at least a year before selling. Proper planning and execution of real estate tax strategies can result in substantial tax savings.
The Power of Depreciation in Real Estate Tax Strategies
Depreciation is one of the most powerful real estate tax strategies available to investors. This tax benefit allows property owners to deduct a portion of the property’s value annually, reducing taxable income. Many investors use depreciation as a core component of their real estate tax strategies to enhance profitability.
One common approach in real estate tax strategies is cost segregation, which accelerates depreciation deductions by breaking down property components into shorter depreciation schedules. By utilizing cost segregation, investors can claim higher deductions in the early years of property ownership. This makes real estate tax strategies even more effective in reducing tax liabilities.
Investors should also be aware of the recapture tax, which applies when a property is sold at a gain. Real estate tax strategies should include a plan to mitigate recapture tax liabilities, such as reinvesting proceeds into new properties through a 1031 exchange. Proper depreciation planning is a key aspect of any comprehensive real estate tax strategy.
1031 Exchanges: A Key to Deferring Taxes
One of the most effective real estate tax strategies for deferring capital gains taxes is the 1031 exchange. This strategy allows investors to reinvest proceeds from a property sale into a similar property without immediately paying capital gains taxes. By leveraging this strategy, investors can grow their real estate portfolio tax-deferred.
A crucial requirement for executing 1031 exchanges as part of real estate tax strategies is the identification of a replacement property within 45 days of selling the original property. The transaction must also be completed within 180 days to qualify for tax deferral benefits. Investors who fail to meet these deadlines may lose the tax advantages of the 1031 exchange.
When incorporating 1031 exchanges into real estate tax strategies, investors should also consider diversification. Swapping into commercial properties, multifamily units, or different geographical areas can enhance investment returns while maintaining tax benefits. Understanding how to execute 1031 exchanges effectively is essential for long-term tax savings.
Maximizing Deductions Through Rental Property Expenses
Smart investors use real estate tax strategies to maximize deductions on rental property expenses. Common deductible expenses include mortgage interest, property taxes, insurance, repairs, maintenance, and property management fees. By tracking and documenting these expenses, investors can reduce taxable rental income.
A significant component of real estate tax strategies is the deduction of home office expenses if the investor manages properties from home. This deduction allows investors to allocate a portion of their home’s expenses, such as utilities and internet costs, toward their business operations. Implementing this strategy can lead to substantial tax savings.
In addition to direct expenses, real estate tax strategies should account for travel-related deductions. Investors who visit their rental properties for maintenance, inspections, or tenant meetings can deduct travel costs, including mileage, lodging, and meals. Keeping thorough records ensures compliance with IRS regulations while optimizing deductions.
Real Estate Professional Status and Tax Advantages
Investors who qualify as real estate professionals can unlock additional real estate tax strategies that allow for greater deductions. The IRS recognizes real estate professionals as those who spend at least 750 hours annually in real estate activities and make it their primary profession. This status grants them the ability to deduct real estate losses against other income.
For many investors, achieving real estate professional status is a game-changer in their real estate tax strategies. Unlike passive investors who are subject to passive loss limitations, real estate professionals can apply rental losses to offset W-2 income or other business earnings. This can lead to substantial tax savings, making it one of the most lucrative real estate tax strategies.
Real estate tax strategies for professionals also include maximizing depreciation deductions and leveraging tax credits. With proper documentation and adherence to IRS rules, real estate professionals can significantly lower their taxable income while building a profitable investment portfolio.
Pass-Through Tax Benefits of Real Estate Investments
Real estate tax strategies often include structuring investments as pass-through entities, such as LLCs or partnerships. Pass-through taxation allows rental income and deductions to flow through to individual investors, avoiding corporate taxes. This structure provides flexibility and tax efficiency.
The Qualified Business Income (QBI) deduction is another essential factor in real estate tax strategies for pass-through entities. Investors who qualify can deduct up to 20% of their rental income, reducing overall tax liability. Proper entity selection ensures that investors maximize this tax benefit.
Incorporating pass-through taxation into real estate tax strategies also provides liability protection. Limited liability companies (LLCs) shield personal assets while offering tax advantages. Choosing the right entity structure is a critical decision in implementing effective real estate tax strategies.
Capital Gains Tax Planning for Real Estate Investors
Effective real estate tax strategies include planning for capital gains taxes when selling properties. Capital gains taxes apply when an investor sells a property for more than its purchase price, but strategic planning can minimize tax exposure.
Holding properties for over a year qualifies for long-term capital gains tax rates, which are lower than short-term rates. Real estate tax strategies should aim to align property sales with long-term holding periods to maximize tax efficiency. Proper timing of property sales is essential in optimizing tax outcomes.
Another real estate tax strategy for reducing capital gains taxes is utilizing installment sales. By structuring property sales to receive payments over time, investors can spread tax liabilities across multiple years. This technique provides tax deferral and improves cash flow management.
Tax Benefits of Short-Term vs. Long-Term Rentals
Real estate investors often debate whether short-term or long-term rentals provide better tax advantages. Understanding the tax benefits of short-term vs. long-term rentals is essential for choosing the right investment strategy. Each rental type has unique tax implications that impact an investor’s net profit.
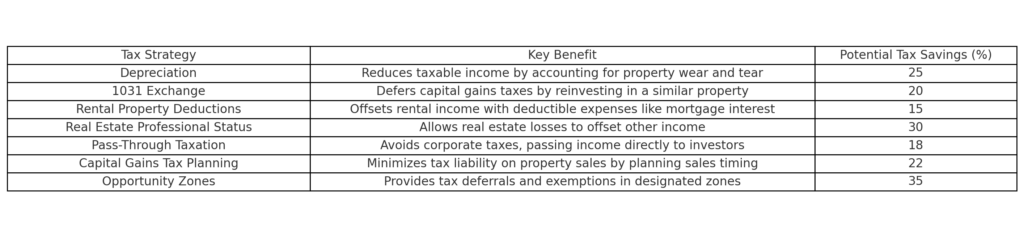
Short-term rentals, such as Airbnb properties, often generate higher rental income due to premium nightly rates. However, they are typically subject to self-employment taxes, and the tax filing process can be more complex. On the other hand, long-term rentals qualify for passive income tax treatment, meaning they are not subject to self-employment tax, making them more tax-efficient.
The table above compares the tax benefits of short-term and long-term rentals, highlighting deductible expenses, depreciation eligibility, and potential tax savings. Investors must weigh these factors to determine which rental strategy aligns with their financial and tax planning goals.
Leveraging Opportunity Zones for Tax Benefits
Opportunity Zones provide significant tax advantages as part of real estate tax strategies. These designated areas encourage investment by offering tax deferrals and exemptions on capital gains. Investors who reinvest gains into Opportunity Zone Funds can benefit from reduced or eliminated taxes on future appreciation.
One of the biggest incentives in Opportunity Zones is the ability to defer capital gains taxes until 2026. This allows investors to reinvest gains tax-free for several years, enhancing long-term growth. Real estate tax strategies that include Opportunity Zone investments can yield substantial savings.
Additionally, holding investments in Opportunity Zones for at least 10 years eliminates capital gains taxes on appreciation. Savvy investors incorporate Opportunity Zones into their real estate tax strategies to maximize wealth accumulation while benefiting from tax incentives.
Tax-Saving Potential of Different Real Estate Ownership Structures
Choosing the right ownership structure for real estate investments can significantly impact tax liabilities. Different entities, such as LLCs, sole proprietorships, S corporations, and C corporations, offer varying levels of tax savings, liability protection, and operational flexibility.
An LLC (Limited Liability Company) is one of the most tax-efficient structures, allowing for pass-through taxation while protecting personal assets. S corporations also provide tax advantages by enabling owners to pay themselves a salary while reducing self-employment taxes. In contrast, C corporations face double taxation but may be beneficial for investors with large-scale operations.
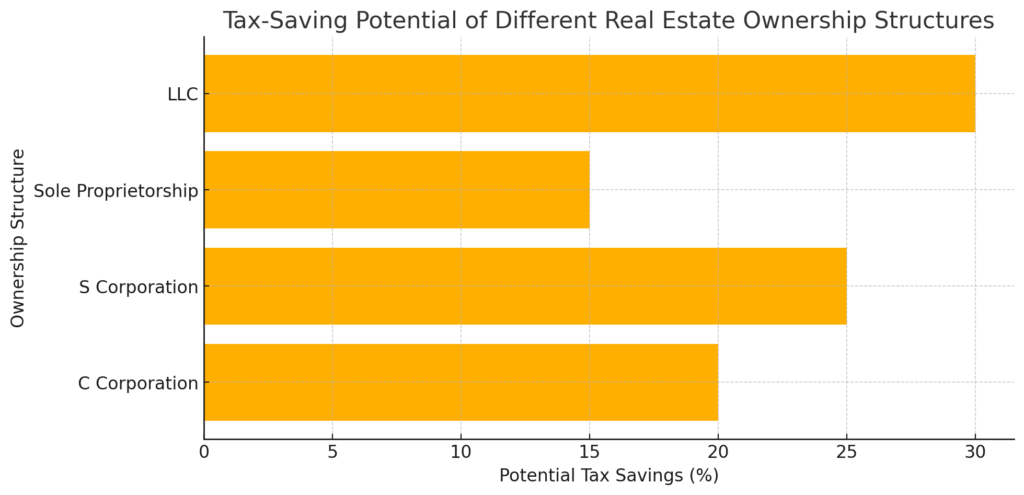
The bar chart above illustrates the potential tax savings of various real estate ownership structures. As seen, LLCs offer the highest tax-saving potential at 30%, followed by S corporations at 25%. Understanding these differences helps investors choose the best structure to maximize tax benefits and protect their investments.
Utilizing Home Office Deductions for Real Estate Investors
Many real estate investors manage their properties from home, making them eligible for home office deductions. This deduction allows investors to write off a portion of their home expenses, including utilities, internet, and mortgage interest, when they use a dedicated space for business purposes. Understanding how to correctly apply for this deduction ensures compliance with IRS regulations while maximizing tax savings.
To qualify, the space must be used exclusively and regularly for managing real estate activities such as bookkeeping, tenant communications, and property research. Investors can choose between the simplified method, which deducts $5 per square foot (up to 300 square feet), or the actual expense method, which accounts for a percentage of household costs. These real estate tax strategies help investors legally lower taxable income while operating efficiently.
However, it’s important to maintain clear documentation of business activities conducted within the home office. Using this strategy incorrectly could trigger IRS scrutiny, so investors should consult a tax professional to ensure eligibility. Properly leveraging the home office deduction is an easy way to save on taxes while running a real estate business.
Tax Benefits of Investing in Multi-Family Properties
Investing in multi-family properties is one of the smartest real estate tax strategies for building long-term wealth while minimizing tax liability. These properties provide multiple rental income streams while offering investors substantial tax deductions, including depreciation, mortgage interest, and maintenance costs. Multi-family investments also qualify for passive income tax treatment, reducing self-employment tax exposure.
One major advantage of owning multi-family properties is the ability to accelerate depreciation using cost segregation studies. By identifying different components of the property (such as appliances, roofing, and HVAC systems), investors can depreciate certain elements faster, leading to larger tax deductions in the early years of ownership. This makes multi-family real estate a tax-efficient investment.
Additionally, multi-family properties qualify for 1031 exchanges, allowing investors to defer capital gains taxes when upgrading to larger or more profitable properties. Whether investing in duplexes, apartment complexes, or townhouses, these properties offer scalable tax benefits that single-family homes may not provide. Understanding the tax advantages of multi-family investing is key to maximizing long-term financial gains.
Estate Planning and Real Estate Tax Strategies
Effective estate planning is an essential part of real estate tax strategies, helping investors pass down assets to heirs while minimizing estate taxes. Without proper planning, real estate assets can be subject to high inheritance taxes, reducing the value passed on to beneficiaries. However, smart tax strategies ensure a smooth and tax-efficient transfer of wealth.
One powerful strategy is setting up a trust to manage real estate holdings. Trusts can help investors avoid probate, reduce estate taxes, and maintain control over asset distribution. Additionally, step-up in basis rules allow heirs to inherit properties at their current market value, eliminating capital gains taxes on past appreciation. This can result in significant tax savings for beneficiaries.
Real estate investors can also leverage gifting strategies to transfer ownership gradually while taking advantage of annual gift tax exclusions. By planning early and consulting estate planning professionals, investors can protect their assets, reduce tax liabilities, and ensure a seamless transition of wealth to future generations.
Final Verdict: Which Investment Strategy is Right for You?
Implementing the right real estate tax strategies can make a massive difference in an investor’s financial success. From leveraging depreciation and 1031 exchanges to maximizing rental property deductions and taking advantage of Opportunity Zones, these strategies help investors keep more of their hard-earned money. Smart tax planning ensures that investors optimize cash flow, lower tax liabilities, and build long-term wealth through real estate investments.
Understanding and applying real estate tax strategies requires staying up to date with tax laws and working with knowledgeable professionals. A tax-efficient investment approach not only enhances returns but also protects investors from unnecessary financial risks. Whether you are new to real estate investing or a seasoned pro, structuring your investments wisely can lead to significant tax savings year after year.
By incorporating these real estate tax strategies into your investment plan, you can take full advantage of the tax benefits available to real estate investors. With careful planning and execution, you can reduce your tax burden, reinvest more into growing your portfolio, and ultimately achieve greater financial freedom. Stay proactive, consult with tax experts, and watch your real estate investments flourish with the right tax strategies in place.
What’s Your Take on Real Estate Tax Strategies?
❓ Are you a strategic tax planner, a long-term investor, or do you prefer short-term rental gains?
💬 Let us know your thoughts in the comments!
Related Topics:
Powerful ways to IoT in Real Estate is Revolutionizing: Unlocking Smart Property Management
Unstoppable AI-Powered Predictive Analytics: Revolutionizing Real Estate for Smarter Investments
Unlocking Blockchain Revolutionary Success in Real Estate Transactions
